Mālus: Latin for apple, a genus of trees and shrubs in the Rosaceae family.
Trivium: Latin for the junction of three roads. It was used in medieval times to describe the education of grammar, logic, and rhetoric.
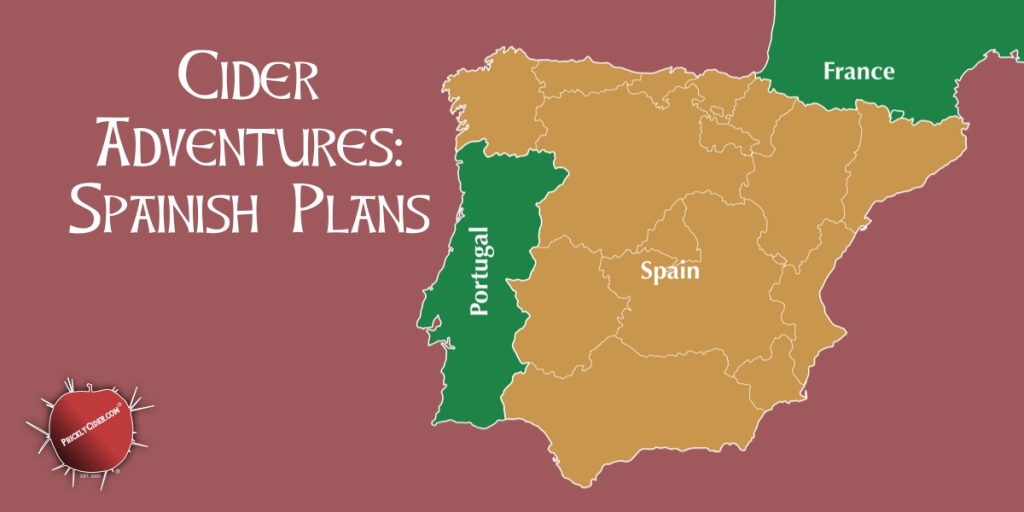
Mālus Trivium is my page intended to provide interesting information and tips about apples and hard cider through a simple visual graphic. To put it simply… it’s apple trivia!
You will continue to see detailed articles and posts on making and enjoying hard cider but Mālus Trivium is all about visual tidbits. Don’t forget my book, which provides even more detailed information about making and enjoying hard cider.
At PricklyCider.com, the goal is to be your source for all things cider.
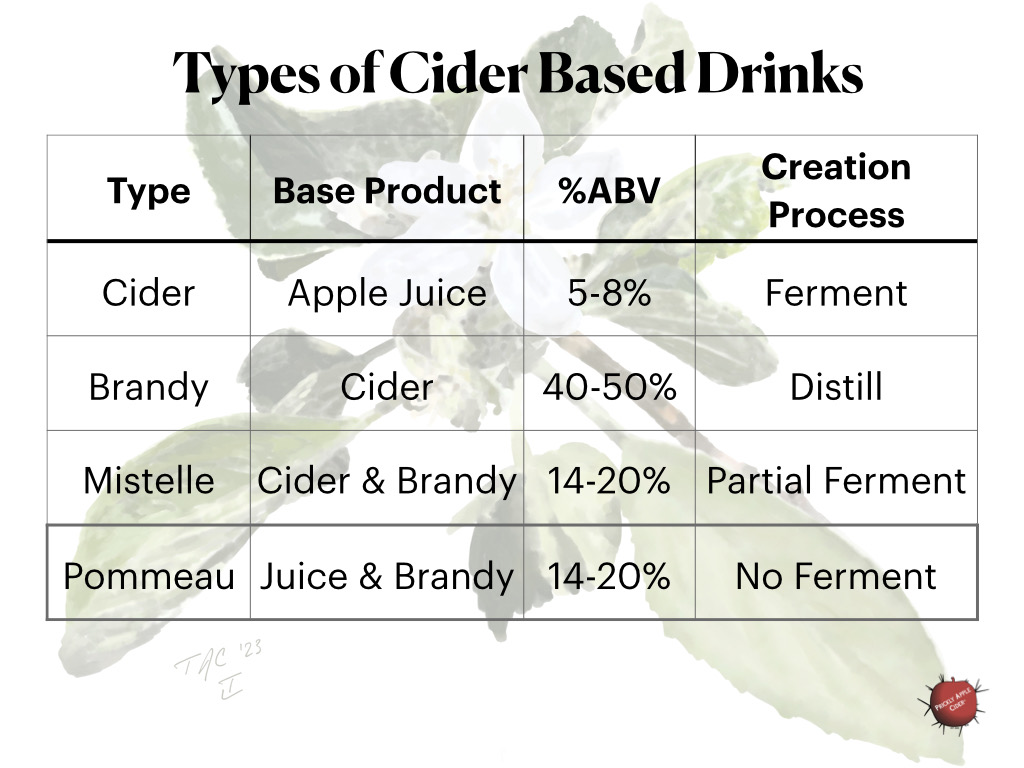
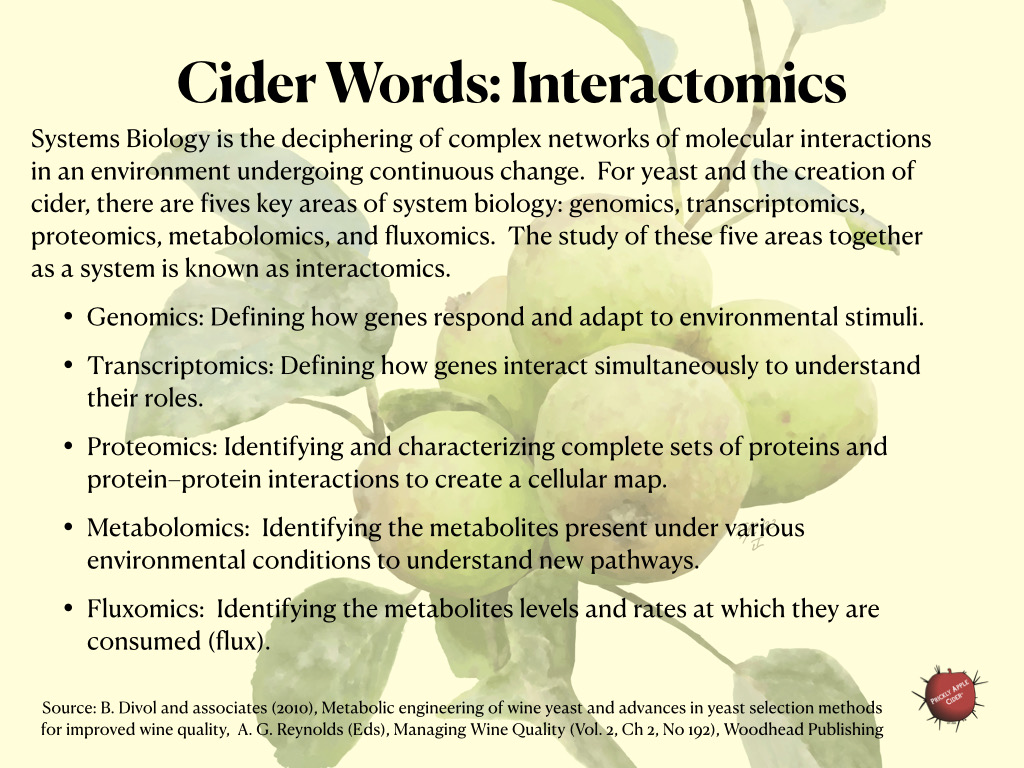





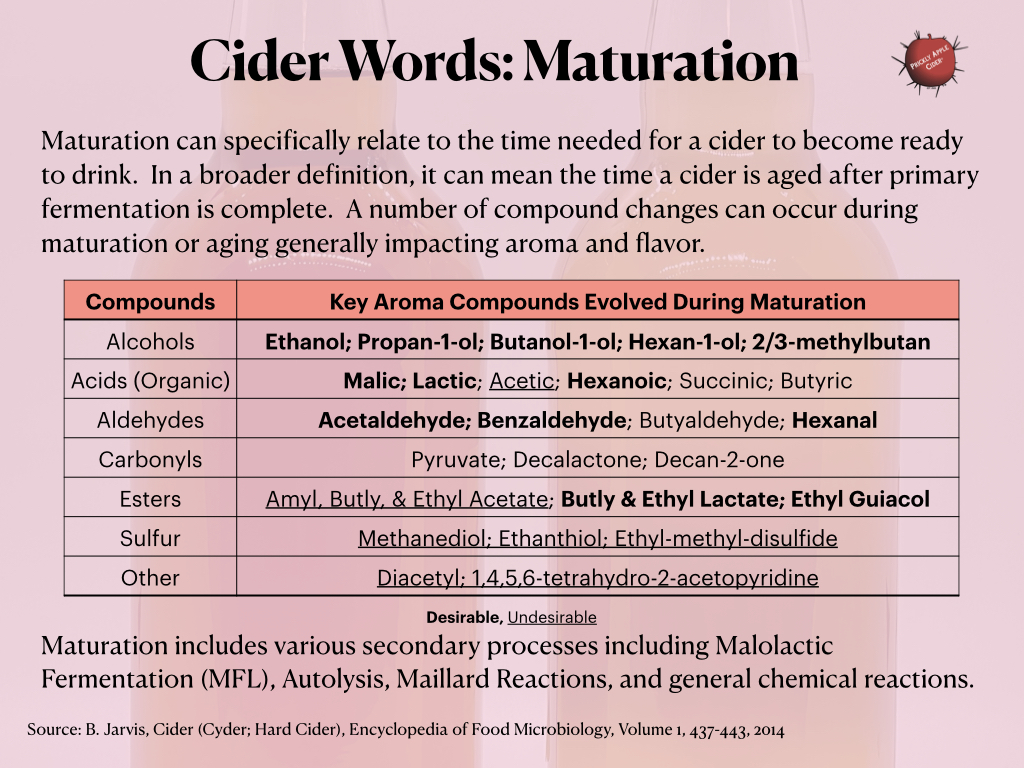








































































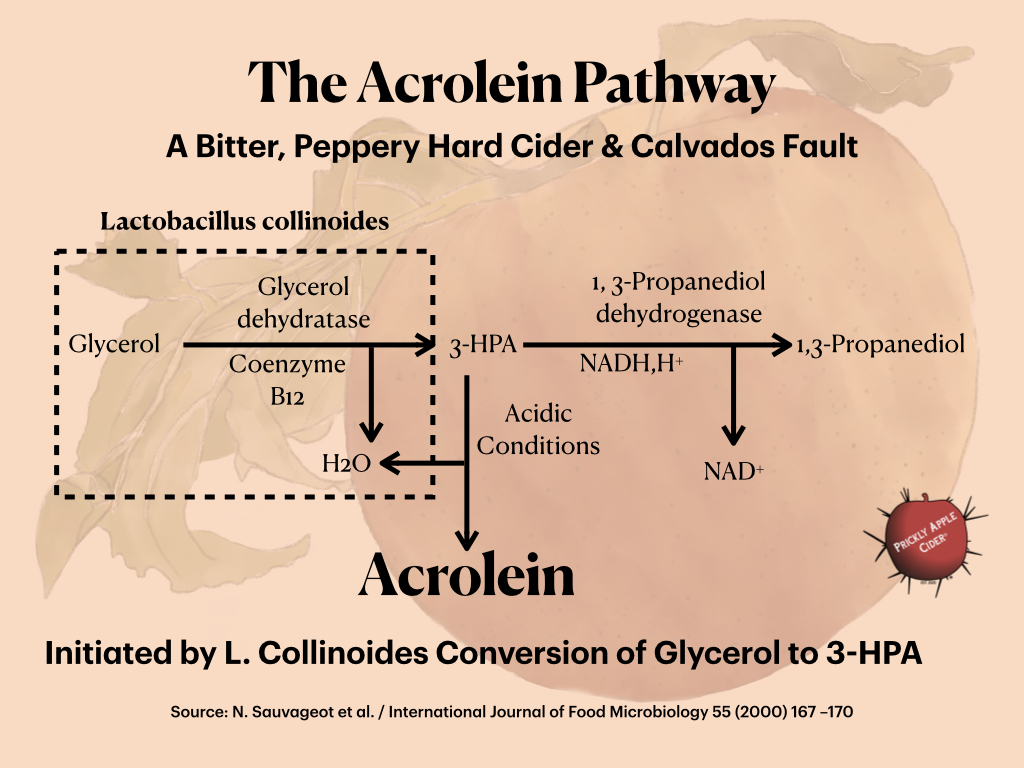


Have questions about making hard cider…
Need some inspiration for a new hard cider recipe…
Interested in exploring how to better enjoy hard cider and pair it with food…
Are you interested in learning more about cider? Follow me to get regular articles about making and experiencing cider.